(Physics) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (1997)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (1997)
General Instructins
-
Attempt all questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
-
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets.
SECTION I (40
Marks)
Attempt all questions from this Section.
Question 1
(a) [4]
-
How fast should a man weighing 60 kg, run so that his kinetic energy is 750 J?
-
A body of mass 1 kg is thrown vertically up with an initial speed of 5 ms-1. What is the magnitude and direction of force due to gravity acting on the body when it is at its highest point?
(b) Diagram 1 alongside shows a weightless lever in equilibrium. Neglect friction at the fulcrum F. [4]
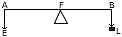
-
State the principle of moments as applied to the alongside lever.
-
Define mechanical advantage and calculate its value for the given lever.
(iii) Name the type of lever which has mechanical advantage greater than 1.
(c) A body weighs 20 gf in air, 18.2 gf in a liquid and 18.0 gf in water. Calculate: [4]
-
the relative density of the body, and
-
the relative density of the liquid.
(d) [4]
-
Define 'specific latent heat of fusion of ice.' Give it's S.I. unit.
-
What is the effect of increase in pressure on the melting point of ice and boiling point of water?
(e) Diagram alongside shows a right-angled prism of refractive index 1·5. An object PQ is placed in front of its base BC. Copy the diagram. [4]
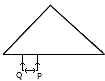
-
Complete the diagram showing the image produced by the prism.
-
Name an instrument in which such a prism is used.
(f) Diagram alongside shows an object AB placed on the principal axis of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens. [4]
![]()
-
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens.
-
Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens.
-
Locate the final image formed.
-
Is the image-real or virtual?
(g) In the nuclear reaction given
below, nucleus X changes to another nucleus Y.
88X226 ——> Y + α + Energy. [4]
-
What is the atomic and mass numbers of Y?
-
Name the gas formed when the α-particle acquires two electrons.
-
What is the effect on the motion of the α-particle when it passes through a region containing a magnetic field?
(h) Diagram alongside shows a circuit containing a coil wound on the long and thin hollow cardboard tube. Copy the diagram. [4]
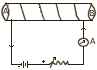
-
Show the polarity acquired by each face of the solenoid.
-
Draw the magnetic lines of force inside the coil and also show their directions.
-
Mention two methods to increase the strength of the magnetic field inside the coil.
(i) Ultra-violet light falls on a dry zinc plate. [4]
-
Name the particles emitted from the plate.
-
What is the nature of charge acquired by the plate?
-
Name the phenomenon that takes place.
-
Name one of the devices based upon the above phenomenon.
(j) [4]
-
Give one example each of the materials suitable for making
a. Fuse wire and
b. Heater element. -
Define angle of dip. At what places on earth will the angle of dip be
a. Maximum?
b. Minimum?
Section II
(40 Marks)
Attempt any four questions fron this Section.
Question 2
(a) A block of mass 30 kg is pulled up a slope (diagram alongside) with a
constant speed by applying a force of 200 N parallel to the slope. A and B are
initial and final positions of the block. [4]
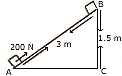
-
Calculate the work done by the force in moving the block from A to B.
-
Calculate the potential energy by the block.
(b) Diagram alongside gives an arrangement of single moving pulleys. Copy the diagram If the effort applied at the free end of the string is E, [3]
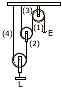
-
Show the direction and magnitude of the forces exerted by the four strings marked (1) to (4).
-
What is the load which can be lifted by the effort?
-
Calculate the mechanical advantage of the system of pulleys.
(c) A block of wood is floating in water. The portion of the block inside water measures 50 cm × 50 cm × 50 cm. What is the magnitude of the buoyancy force acting on the block? [3]
Question 3 [3]
(a) A piece of metal at 10°C has a mass of 50 g. When it is placed in a current of steam at 100°C, 0.7 g of steam is condensed on it. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. Given: Latent heat of steam = 540 cal/g
(b) Explain briefly:
-
Why hot water bottles are very efficient for fermentation?
-
How human body temperature is maintained at normal value (37°C) when the atmospheric temperature rises as high as 45°C?
Question 4
(a) [6]
-
State Snell's law of refraction of light.
-
Diagram shows a glass prism placed in minimum deviation position. A ray of monochromatic light is incident on its face AB. Copy the diagram and show the refracted ray and the emergent ray. Mark the angle of deviation. State any two factors on which the angle of deviation depends.
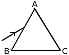
(b) [4]
-
Define dispersion of light.
-
Explain briefly how white light gets dispersed by a prism.
-
What is an impure spectrum?
Question 5
(a) [6]
-
State any two characteristics of a wave motion.
-
What is the relation between frequency, wavelength and speed of a wave?
-
A longitudinal wave of wavelength l cm travels in air with a speed of 330 m/s. Calculate the frequency of the wave. Can this wave be heard by a normal human being?
(b) Two waves A and B have wavelengths 0·01 Å and 9000 Å respectively. [4]
-
Name the two waves.
-
Are the speeds of these two waves equal when they travel in vacuum?
-
If the amplitude of a wave is doubled what will be the effect on its loudness?
Question 6
(a) Given alongside is the circuit diagram in which three resistances 1Ω, 2Ω
and 3Ω are connected to a cell of emf 2 V and internal resistance 0.5Ω.
[6]
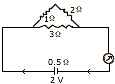
-
Calculate the total resistance of the circuit.
-
What is the reading of the ammeter?
-
What will be the ammeter reading if an exactly similar cell is connected in series with the given cell?
(b) [4]
-
Draw a neat labelled diagram of an a.c.generator.
-
What is the magnitude of the emf induced in the coil when its plane becomes parallel to the magnetic held?
Question 7
(a) [6]
-
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier using two diodes.
-
Why is diode called a valve?
-
Draw two diagrams one above another, one showing the input and the other showing the output in the above case A.
(b) [4]
-
Draw a neat labelled diagram of modern X-ray tube.
-
What is the mechanism of energy production in a fission reaction?