(Physics) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (1996)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (1996)
General Instructions
-
Attempt all questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
-
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets.
SECTION I (40
Marks)
Attempt all questions from this Section.
Question 1
(a) [4]
-
Explain briefly why a balloon filled with helium gas rises in air. Why does the balloon rise to a particular height above the ground and does not rise further?
-
An ice-berg floats in fresh water with a part of it outside the water surface. Calculate the fraction of volume of ice-berg which is below the water surface. Given: Density of ice = 917 kg m-3. Density of fresh water = 1000 kg m-3
(b) [4]
-
Relative density of silver is 10.8. What is the density of silver in S.I. Unit?
-
Diagram given alongside, shows refraction and emergence of a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab. Copy the diagram and mark the lateral displacement of the incident ray. Name the two factors on which the lateral displacement depends.
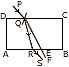
(c) Two parallel rays of light enter the eye of a person suffering from myopia as shown in the diagram given alongside. Copy the diagram and [4]
-
Complete the ray diagram to show where the image is formed;
-
Name the type of lens required to correct the defect; and
-
Draw the diagram again showing the position of the correcting lens, two parallel rays to the lens and the position of the final image.
(d) An object AB is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens as shown alongside in diagram. Copy the diagram. Using three rays starting from B and the properties of the points marked F1, O and F2; obtain the image formed by the lens (F1 and F2 are the foci). [4]
![]()
(e) [4]
-
Define a pair of complementary colours. Name the colours in one such pair.
-
Fill in the blanks in the following:
a . A red rose appears .......... when seen in green light.
b. Red + Blue = ........
(f) [4]
-
Define 1 watt and] kWh.
-
Convert 1 kWh into joules.
(g) An electric bulb is marked 220 V, 100 W. The bulb is connected to a 220 V supply. [4]
-
Calculate: 1. resistance of the filament; 2. current flowing through the filament.
-
Is the filament resistance of the glowing bulb greater, smaller or the same compared to its resistance when it is not glowing?
(h) There are three pins in an electric plug, answer the following: [4]
-
How would you identify the earth pin?
-
In which of the three connecting wires should a switch be connected?
-
Explain why a switch should not be touched with wet hands.
(i) A given liquid changes into the gaseous state at a fixed temperature as well as at all temperatures. [4]
-
Name the process that takes place in each of the above two cases.
-
Mention two points of difference between the two cases in (i) above.
(j) State the energy changes which take place while using the following: [4]
-
A microphone;
-
An electric bulb; and
-
A steam engine.
SECTION II
(40 Marks)
Attempt any four questions from this Section.
Question 2
(a) [6]
-
Define the S.I. unit of force. Obtain a relation between the S.I. unit and the C.G.S. unit of force.
-
A man of mass 60 kg runs up a flight of 30 steps in 15 seconds. If each step is of 20 cm high, calculate the power developed by the man. Take g = 10 ms-2.
(b) [4]
-
Define work and its S.I. unit.
-
Write an expression for the work done by a constant force acting on a body that gets displaced from its initial position in a direction different from the direction of the force.
-
Give an example when work done by a force acting on a body is zero even through the body gets displaced from its initial position by the application of the force.
Question 3
(a) Diagram given alongside shows an arrangement of four pulleys A load L is
attached to the movable lower block and effort E is applied at free end of the
string. Copy the diagram. and: [4]
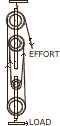
-
Draw arrows to indicate tension in each part of the string; and
-
Calculate the mechanical advantage of the system.
(b) [6]
-
Define specific heat capacity of a material.
-
A 30 g ice cube at 0°C is dropped into 200 g of water at 30°C. Calculate the jinal temperature of water when the entire ice cube has melted. Given: Latent heat of ice = 80 cal g−l; Specific heat capacity of water = 1 cal g-1 (°C)-1.
Question 4
(a) [5]
-
Define refractive index of a medium with respect to air.
-
Calculate the speed of light in water. Given: Speed of light in vacuum = 3 10-8 ms−1, and refractive index of water = 4/3.
-
Calculate the power of a convex lens of focal length 25 cm.
(b) In the diagram given along side, a source of light S is placed at the bottom of a beaker containing water. [5]
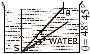
-
Copy the diagram and show the path of rays marked with arrows, after they meet the water-air boundary.
-
Does the ray, marked with one arrow, undergo refraction?
-
Name the phenomenon exhibited by the ray marked with three arrows.
-
State the conditions necessary for the phenomenon in (iii) above.
Question 5
(a) [6]
-
Define the phenomenon of resonance.
-
A stretched wire 0.5 m long is made to vibrate in two different modes as shown in diagram (A) and (B) given below:
1. If the wavelength of the wave produced in mode (A) is 1 m, what is the wavelength of the wave produced in mode (B) of the following diagram?
2. In which case is the note produced louder? Give a reason for your answer.
3. In which case is the pitch of the note produced is higher? Give a reason for your answer.
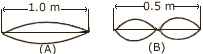
(b) [4]
-
A TV station transmits waves of frequency 200 MHz. Calculate the wavelength of the waves, if their speed in air is 3.0 × 108 ms-1.
-
Give the approximate range of wavelengths in vacuum associated with U-V rays and visible light.
Question 6
(a) [6]
(i) Write an expression for the resistance of a conducting wire in terms of its length and area of cross-section.
(ii) Two resistors of resistances 3Ω and 2Ω in parallel are connected to a cell of end 1.5 V and internal resistance 0.3Ω. Draw a labelled circuit diagram showing the above arrangement and calculate the current drawn from the cell.
(b) [4]
-
Name the principle on which functioning of a transformer depends.
-
What is the function of a step-up transformer?
-
Can a transformer work when it is connected to a d.c. source?
-
Diagram given alongside shows schematically part of a step-down transformer. Draw the complete diagram in your answer sheet.
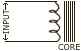
Question 7
(a) [4]
-
State the mechanism of production of X-rays. Give two importance of X-rays
-
What is the photoelectric effect? Draw a neat labelled diagram of a photoelectric cell.
(b) [6]
-
Define nuclear fusion and state the necessary conditions for the same.
-
Why is energy released in a nuclear fusion reaction?