(Biology) Paper : AIPMT 2007 Biology Mains (Part -1)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper
: AIPMT 2007 Biology Mains (Part -1)
All India Pre-Medical / Pre-Dental Entrance Examination
Q. 1. Write the location and function of the following
- Cytoskeleton
- Phytol chain
- Synergid
- Sieve tube element
- Centromere
Sol.
- Location– Cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell.
Function– Support to the cell - Location– Chlorophyll
Function– Anchors the chlorophyll molecule into the lipid part of thylakoid membrane. - Location– Embryo sac
Function– Secreting chemotactically active substance for attracting pollen tube and forming seat for pollen
tube discharge. - Location– Phloem
Function– Translocation of solute - Location– Chromosome
Function– Attachment of spindle fibres.
Q. 2.
| (a) |
What is shown in diagram (a)? |
(b) |
Tell whether it is T1- phage or T2- phage? |
| (c) |
Which type of ovule is this? |
(d) |
What is this type of flower called? |
| (e) |
Which type of aestivation is this? Give examples? |
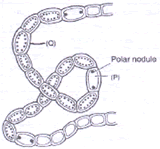
- Nostoc ; (P) = Heteroayst; (Q) = Akinete
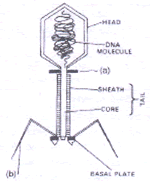
- T2 -phage, (a) collar, (b) Tail fibre
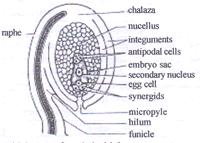
- Anatropous ovule, Body of the ovule is inverted.
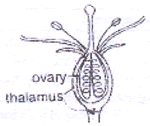
- Epigynous flower, e.g., Cucurbitaceae, Asteraceae
- Vexillary or des cending imbricate, e.g., Soyabean, Gram, Crotolaria, etc.
Q. 3. Write down the types of placentation, inflorescence and fruit of the following
- Pea
- Coriander
- Wheat
- Sunflower
- Mustard
Sol.
| S. N. | Plant | Placentation | Inflorescence | Fruit |
| (a) | Pea | Marginal | Solitary axillary or terminal, raceme | Pod orlegume |
| (b) | Coriander |
Axile |
Compound umbel | Ceremocarp |
| (c) | Wheat | Basal | Spike of spike of spikelet | Caryopsis |
| (d) | Sunflower | Basal | Capitulum | Cypsela |
| (e) | Mustard raceme | Parietal | Corymbose | Siliqua |
Q. 4. Differentiate between the following [Give one important difference]
- Culm and Caudex
- Slime moulds and fungi
- Cyathium and hypanthodium
- Biological magnification and eutrophication
- White rust and Brown rust
Sol.
|
(a) |
Culm |
Caudex |
|
|
Joint stem with solid nodes and hollow |
Unbranched cylindrical stem with crown of leaves at apex. Marked with scars of fallen leaves e.g., Coconut |
|
(b) |
Slime moulds |
Fungi |
|
|
Vegetative cell without cell wall but spores with cellulosic cell wall |
Vegetative cell with cell wall made up of either fungal cellulose or chitin or both. |
|
(c) |
Cyathium |
Hypanthodium |
|
|
Peduncle terminates into a single female flower. It is surrounded by
a large number of male flowers in scorpoid |
Main axis forms a flesly cup-shaped receptacle. It has an apical
opening called ostiole. Unisexual flowers |
|
(d) |
Biological magnification |
Eutrophication |
|
|
Non-biodegradable pesticides pass into food chain and increase in
amount per unit weight of organisms with the rise in trophic level due
to their accumulation in fat tissue. The phenomenon is called |
Due to run off from fields, lawns and detergent rich sewage into the
water body there is nutrient enrichment of the water body. The
phenomenon is |
|
(e) |
White rust |
Brown rust |
|
|
It is a fungal disease caused by Cystopus candidus or Albugo candidaon vegetative parts of crucifers. |
It is a fungal disease caused by Puccinia reconditaon vegetative parts of wheat plant. |
Q. 5. Match the column-I and Column-II
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
(a) Jacob and Monod |
(i) Neurospora |
|
(b) One gene one enzyme hypothesis |
(ii) Operon |
|
(c) Griffith |
(iii) Reverse Transcriptase |
|
(d) Temin and Baltimore |
(iv) Okazaki fragments |
|
(e) DNA polymerase |
(v) Transformation |
|
|
(vi) Transduction |
|
|
(vii) Conjugation |
Sol. (a) – (ii), (b)– (i), (c) – (v), (d) – (iii) , (e)– (iv)
Q. 6. Fill in the blanks with suitable words given in boxes:
|
Marsilea |
Coralloid root |
Usnea |
Eichhornia |
|
|
Monoecious |
Pneumatophores |
Geitonogamy |
Cycas |
|
|
Pinus |
Dioecious |
Vivipary |
Xenogamy |
Oscillatoria |
- Rhizophorahas both _______________________and _________________
- (b) Aquatic plants are ______________________(Pteridophyte) and_______________________(Angiosperm)
- (c) Plant bearing both male and female flowers is called______________and
the pollination between different
flowers of the same plant is called_______________. - ____________has ______________.
Sol.
- Pneumatophores, Vivipary
- Marsilea, Eichhornia
- Monoecious, Geitonogamy
- Cycas, Coralloid root
Q. 7.
- Give any two conditions for seed habit.
- Which of these shows tendency of seed habit?
Lycopodium
Equisetum
Selaginella
Pteris
Dryopteris
Pteridiun
- Suggest three ways to break seed dormancy.
Sol.
- Heterospory, formation of female gametophyte inside magasporangium.
- Selaginella
- Mechanical scarification, stratification, impaction.
Q. 8. Fill in the blanks
- Mutation can be defined as ______________________________variation.
- Mutation leads to evolution of _____________________ of a gene.
- Genes expressed only in homozygous state are_____________________.
- When both alleles of a gene are expressed it is __________________.
- Gene, which is most frequent is ________________type.
Sol.
- Sudden heritable
- New alleles
- Recessive
- Codominance
- Wild type
Q. 9.
- Who discovered photoperiodism?
- Select one SDP and one LDP from following plantsChrysanthemum , Rice, Spinach, Barley, Radish
- Who gave the term ‘Phytochrome’? Give one specific feature of phytochrome.
Sol.
- Garner and Allard
- SDP – Chrysanthemum
LDP – Spinach - Borthwick, Induction of flowering
Q. 10. Match the Column-I and Column-II
|
Column-I |
Column-II |
|
(a) Indian Rhinoceros |
(i) Extinct |
|
(b) Acid rain |
(ii) Endangered |
|
(c) Somaclonal variations |
(iii) Gir forest |
|
(d) Protoplasm fusion |
(iv) Corbett National Park |
|
(e) Biopiracy |
(v) CFC |
|
(vi) Nitrogen oxide |
|
|
(vii) Sulphur oxide |
|
|
(viii) PEG |
|
|
(ix) Mutation |
|
|
(x) Tumeric |
Sol. (a)– (iv), (b)–(v), (c)–(xi), (d)– (viii), (e)–(x)
Q. 11.Differentiate between
- Habitat and Niche
- Flora and Vegetation
| (a) |
Habitat |
Niche |
| Habitat is a place where an organism lives.
It represents a particular set of environmental conditions suitable for
its successful growth. |
Niche represents not only the place where an organism lives but the range of conditions and resource qualities within which a species can survive and reproduce. | |
|
(b) |
Flora |
Vegetation |
| Total number of plant species found in an area constitutes it’s flora. | Types of plants found in an area constitute the vegetation of the area e.g., Xerophytic vegetation is found in deserts. |