(Physics) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (2004)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (2004)
General Instructions
- Section I is compulsory. Attempt any four questions from Section II.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brakets.
SECTION I (40 Marks)
Attempt all questions from this Section
Question 1
(a) (i) Explain why scissors for cutting cloth may have blades much longer than the handles; but shears for cutting metals have short blades and long handles.
(ii) A woman draws water from a well using a fixed pulley. The mass of the bucket and water together is 6.0 kg. The force applied by the woman is 70 N. Calculate the mechanical advantage. (Take g = 10 m/s2) [4]
(b) (i) State the energy changes in an oscillating pendulum.
(ii) Two balls of mass ratio 1 : 2 are dropped from the same height.
- State the ratio between their velocities when they strike the ground.
- The ratio of the forces acting on them during motion. [4]
(c) (i) A piece of ice floating in a glass of water melts but the level of water in the glass does not change. Explain this phenomenon.
(ii) An inflated gas balloon is placed in a jar which is connected to an evacuating pump. What will be observed if the air inside the jar is pumped out? Give a reason justifying your answer.[4]
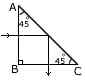
(d) (i) Define 'critical angle.'
(ii) A ray of light passes through a right angled prism as shown in the figure. State the angles of incidence at the faces AC and BC.[4]
(e) (i) 1. White light is passed through a yellow fillter. What colour is (colours are) seen on a screen placed at the end?
2. If the light emerging from the yellow filter is then passed
through a red filter, what will be seen on the screen placed at the
end?
(ii) What is Sonar? State the principle on which it is based.[4]
(f) (a) Differentiate between resonance and forced vibrations.
(ii) The wavelength of waves produced on the surface of water is 20 cm. If the wave velocity is 24 ms-1, calculate :
- The number of waves produced in one second and
- The time required to produce one wave.[4]
(g) (a) State the purpose of a fuse in an electric circuit. Name the material used for making a fuse wire.
(b) Mention two factors on which the internal resistance of a cell depends.[4]
(h) (a) Draw a labelled diagram to show the various components of a step-down transformer.
(b) State the main difference between a step-up and step-down transformer.[4]
(i) (i) In winter, the weather forecast for a certain day was 'severe frost'. A wise farmer watered his yields the night before to prevent frost damage to his crops. Why did he water his fields?
(ii) 10125 J of heat energy boils off 4.5 g of water at 1000C to steam at 1000C. Find the specific latent heat of steam.[4]
(j) (a) Define the term 'Work function' of a metal.
(b) Mention two common properties of gamma radiations and visible light.[4]
SECTION - II (40 Marks)
Answer any four questions from this section
Question 2
(a) State Newton's second law of motion both in words and in equation form. Under what condition does this equation become F = ma? [4]
(b) The radius of the driving wheel of a set of gears is 18 cm. It has 100 teeth and rotates at a speed of 30 rpm. The driven wheel rotates at a speed of 150 rpm. Calculate:
- The gear ratio.
- The number of teeth on the driven wheel.
- The radius of the driven wheel.[4]
(c) A ball of mass 0.20 kg is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. Calculate the maximum potential energy it gains as it goes up.[2]
Question 3
(a) (i) State 'Archimedes' Principle.
(ii) A cargo ship is loaded in sea water to maximum capacity. What will happen if this ship is moved to river water? Give a reason for your answer.
(iii) A body of mass 100 g is floating in water. What will be its apparent weight ? Justify your answer. [5]
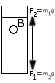
(b) A small stone of mass m = 200g is held under water in a tall jar and allowed to fall as shown in the figure. The free body diagram of the stone is also shown.
- What do F2 and ml represent?
- Calculate the net force acting on the stone and
- Its acceleration, as it falls through water. (Neglect the force due to viscosity. Take the volume of the stone as 80 cm3, density of water as 1.0 g/cm3 and the acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s2.) [5]
Question 4
(a) The diagram given below shows an object O and its image I. Copy the diagram and draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus. Name the type of lens in this case. [4]
(b) (i) State Snell's law.
(ii) Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 ms-1) [4]
(c) (i) What is an optical fibre?
(ii) Give one practical use of an optical fibre. [2]
Question 5
(a) A thermos flask of negligible heat capacity contains 100 g of ice and 30g of water.
(i) Calculate:
- The mass of steam at l000C needed to condense in the flask to just melt the ice;
- The amount of water in the flask after condensation.
(Specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2260 J/g
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J/g
Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g0C.) - Is it possible to condense the water formed, back to ice by adding ice at 00C? Explain, giving a suitable reason to justify your answer. [6]
(b) (i) State the principle of calorimetry.
(ii) Express l kWh in terms of S.I . unit of energy.
(iii) Which of the two, 1 g of ice at 00C or 1 g of water at 00C contains more heat? Give a reason for your answer.[4]
Question 6
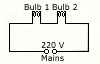
(a) An electric bulb rated 220 V, 60W is working at full efficiency.
- State the resistance of the coil of the bulb.
- Another identical bulb is connected in series with the first one and the system is connected across the mains as shown below.
(1) State the rate of conversion of energy in each bulb.
(2) Calculate the total power.
(3) What will be the total power, if the bulbs are connected in parallel? [6]
(b) Explain briefly how a magnet, can be demagnetised using an alternating current? [2]
State two ways by which the emf in an A.C. generator can be increased. [2]
Question 7
(a) (i) Copy and complete the below diagram by showing and labelling the paths of alpha, beta and gamma radiations in an electricfield.
(ii) Name the radiations which have the least penetrating power.[4]
(b) (i) Give one difference between a chemical change and a nuclear change.
(ii) How is the cathode ray tube used to convert an electrical signal into a visual signal? [3]
(c) Copy and complete the following nuclear equations by filling in the correct values in the blanks. [3]
92P238 |
-α → |
...P1... |
-β → |
...P2... |
-β → |
...P3... |