(Important Topics) Biology: Structure of DNA -A Double Helix
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in

Important Topics Biology: Structure of DNA -A double helix
DNA – A double helix
- DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic
acid.It is a nucleic which is used for
storing information for long
term in all living beings and
some viruses.
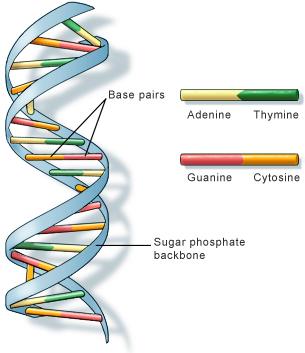
- Base composition in DNA varies from one
species to other but in all the cases
the amount of adenine is equal to thymine and the amount of
cytosine is equal to guanine.
- The total amount of purines
is always equal to pyrimidines.
A + G = C + T
Ratio AT/CG varies between the species.
In man this ratio is 1.52
In E Coil the ratio is 0.93
- The double helix is
composed of two right handed helical polynucleotide chains coiled around the
same central axis.
- The two strands are held together by
hydrogen bonds.
- The two strands are antiparallel i.e. 5′ ——> 3′
phosphodiester linkages running in opposite directions.
- Two hydrogen bonds are formed between A and T
and three are formed between C and G.
- In addition to hydrogen bonds
other forces like hydrophobic interactions between stacked bases are also
responsible for the stability and maintenance of double helix.
- The diameter of double helix is 2nm and the double
helical structure repeats at an interval of 3.4nm which corresponds to
ten base pairs.
- DNA helices can be right handed or left handed. But the
b – conformation of DNA having the right handed helices is
the most stable.
- On heating the two strands of DNA separate from each other and on
cooling these again hybridize.
- The temperature at which the two strands separate completely is known as
melting temperature (Tm). Melting temperature is specific
for each specific sequence
- The B sample of DNA having higher melting point must have more C-G
content because C-G pair has 3 hydrogen bonds.
- The sequence of bases along the DNA molecule encodes for the sequence of amino acids in every protein in all organisms.