(Paper) CBSE Class XII : Physics Exam Paper Year 2009 (ISC Board)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
CBSE Class XII : Physics Exam Paper Year 2009 (ISC Board)
(Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must not start writing during this time)
General Instruction:
(i) Answer all question in Part I and six questions from Part II,
choosing two questions from each of the Section A, B and C.
(ii). All working including rough work should be done on the same sheet as, and
adjacent to the rest of the answer.
(iii). The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in
brackets []. (Material to be supplied: Log tables including Trigonometric
functions)
(iv). A list of useful physical constants is given at the end of this paper.
PART I (Compulsory)
Q1.Answer all question briefly and to the point:
(i) Explain the statement ‘Relative permittivity of water is 81’.
(ii) Draw (at least three) electric lines of force due to an electric
dipole.
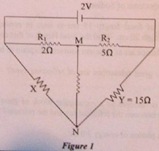
(iii) Find the value of resistance X in the circuit below so that the
junction M and N are at the same potential.
(iv) When the cold junction of a certain thermo-couple was
maintained at 20 degree C, its neutral temperature was found to be 180 degree C.
Find its temperature of inversion.
(v) State how the magnetic susceptibility of a ferromagnetic change
when it is heated.
(vi) Write an equation of Lorentz force F acting on a charged particle
having charge q moving in a magnetic field B with a velocity v in vector form.
(vii) What is the value of power factor in a series LCR circuit at
resonance?
(viii) An a.c. generator generates an emf ‘e’ given by : e = 311 Sin
(100 pai t) volt. Find the rms value of the emf generated by the generator.
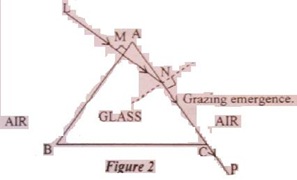
(ix) A ray LM of monochromatic light incident normally on one
refracting surface AB of a regular glass prism ABC emerges in air from the
adjacent surface AC as
shown in Figure. Calculate the refractive index of the material of the prism.
(x) Describe the absorption spectrum of Sodium.
(xi) A thin converging lens of focal length 15 cm is kept in contact
with a thin diverging lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the focal length of this
combination.
(xii) Can two sodium vapour lamps act as coherent sources? Explain in
brief.
(xiii) Why all over the world, giant telescopes are of reflecting type?
State any one reason.
(xiv) A ray of ordinary light is incident on a rectangular block of
glass at Brewster’s angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the
refracted ray of light?
(xv) Find the momentum of a photon of energy 3.0 eV.
(xvi) The half life of a certain radio active element is 8 hours. if a
pupli starts with 32 g of this element, how much of the sample will be left
behind at the end of one day?
(xvii) If a hydrogen atom goes from III excited state to 11 excited
state, what kind of radiation (visible light, ultra violet, infrared, etc.) is
emitted?
(xviii) Where in our universe is the thermo-nuclear energy being
released naturally?
(xix) In which of the solids (semi-conductors, conductors or
insulators) do conduction band and valence band overlap?
(x) What is the symbol of a NOR gate?
PART II SECTION A
Q2(a) With the help of a labeled diagram, obtain an
expression for the electric field intensity ‘E’ at a point P in broad side
position (i.e. equatorial plane) of an electric dipole.
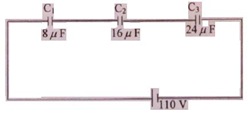
(b) Find the electric charge Q1 on plate of capacitor C1, shown in
Figure below:
(c) (i) What is meant by:
(1) Drift velocity and
(2) Relaxation time?
(ii) A metallic plug AB is carrying a current 1 (see Figure below). State how the drift velocity of free electrons varies, if at all, from end A to end B.
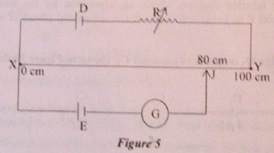
Q3. (a) Figure below shows a uniform manganin wire XY of length 100 cm and resistance 9 ome, connected to an accumulator D of emf 4V and internal resistance 1 ome through a variable resistance R, E is a cell of emf 1.8 V connected to the wire XY via a jockey J and a central zero galvanometer G. It is found that the galvanometer shows no deflection when XJ = 80 cm. Find the value of R.
(b) Obtain an expression for magnetic flux density ‘B’ at
the center of a circular coil of radius R and having N turns, when a current I
is flowing through it.
(c) (i) State any two differences between a moving coil galvanometer
and a tangent galvanometer.
(ii) What is the use of a Cyclotron?
Q4. (a) What is meant by the time constant
of an LR circuit? When the current flowing through a coil P decreases from 5A 0
in 0.2 seconds, an emf of 60V is induced across the terminals of an adjacent
coil Q. Calculate the coefficient of mutual inductance of the two coils P and Q.
(b) When an alternating ernf e = 300 Sin (100
n t + n/6)
volt is applied to a circuit, the current I through it Is I = 5.0 Sin (100
n t + n/6) ampere. Find the:
(i) Phase difference between the emf and the current.
(ii) Average power consumed by the circuit.
SECTION –B (Answer any two questions)
Q5. (a) In which part of’ the
electromagnetic spectrum, do the following radiations lie:
(i) Having wavelength of 20 nm
(ii) Having frequency of 10 MHz
(b) In Young’s double slit experiment, what is meant by
‘fringe width’ or ‘fringe separation’? State two ways of increasing the fringe
width, without changing the source of light.
(c) A thin convex lens which is made of glass (refractive index 1.5)
has a focal length of 20 cm. It is now completely immersed in a transparent
liquid having refractive index 1.75. Find the new focal length of the lens.
Q6.(a) Draw a labeled graph showing the variation in
intensity of light with distance in a single slit Fraunhofer diffraction
experiment.
(b) Give any two methods by which (ordinary) light can be polarised.
(c) A point source of monochromatic light ‘S’ is kept at the center C
of the bottom of a cylinder. Radius of the circular base of the cylinder is 50.0
cm. The cylinder contains water (refractive index=4/3) to a height of 7.0 cm.
(see Figure below):
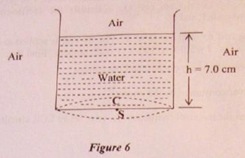
Find the area of water surface through which light emerges in air.(Take n = 22/7)
Q7. (a) An astronomical telescope consists of two convex lenses having focal length 80 cm and 4 cm. When it is in normal adjustment, what is its:
(i) Length,
(ii) Magnifying power?
(b) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm is to be used as a simple microscope. Where should an object be kept so that image formed by the lens lies at least distance D of distinct vision (D=25 cm)? Also calculate the magnifying power of this instrument in this set up.
(c) What is meant by ‘Chromatic aberration’? A thin convex lens of focal length 30 cm and made of flint glass (dispersive power = 0.03) is kept in contact with a thin concave lens of focal length 20 cm and made of crown glass. Calculate the dispersive power of crown glass if the above said combination acts as an achromatic doublet.
SECTION C (Answer any two questions)
Q8.(a) Electrons, initially at rest, are passed through a
potential difference of 2 kV.
Calculate their:
(i) Final velocity and
(ii) de Broglie wavelength
(b) What are characteristic X rays? How are they different
from continuous X rays? Give any one difference.
(c) Wavelength of the Ist line (Ha) of
Balmer series of hydrogen is 656.3 nm. Find the wavelength of its 2nd line (Hb).
Q9. (a) Plot a labeled graph of |Vs| where Vs is stopping potential of photoelectrons versus frequency ‘f’ of incident radiation. How will you use this graph to determine the value of Planck’s constant? Explain.
(b) (i) Define ‘unified atomic mass unit’.
(ii) Find the minimum energy which a gamma ray photon
should possess so that it is capable of producing an electron positron pair.
(c) Fission of U – 235 nucleus releases 200 MeV of energy. Calculate the fission rate (i.e. no. of fissions per second) in order to produce a power of 320 MW.
Q10.(a) Draw a neatly labelled circuit diagram of a Full Wave rectifier using two Junction diodes.
(b) A sinusoidal voltage c = ro Sin
(wt) is fed to a common emitter amplifier. Draw neatly labelled diagrams to
show:
(i) Signal voltage
(ii) Output voltage of the amplifier.
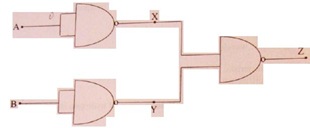
(c) Make a truth showing input at A and B and output at X, Y and Z for
the combination of gates shown in Figure below.