(Geography) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Geography (1997)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Geography (1997)
General Instructins
-
Section A is compulsory. All questions from Section A are to be attempted.
-
Answer any two questions from Section B,answer any two questionsfrom Section C and Section D. The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets.
SECTION - A
Attempt all questions from this Section.
Question 1
(a) In which quarter will you look for the lowest contour in the extract of the toposheet which has been provided to you? Why should it be in this quarter? [2]
(b) Write down the lowest and the highest spot heights found on this map. State whether they are in metres or in feet. [2]
(c) Give a six-figure grid reference for the peak of Bhuni-Magri Hill. Also State the grid number in which the hill is located. [2]
(d) In what compass direction does the village Pamera lie in respect of Gulabganj? How many kilometres is PAMERA from Gulabganj? [2]
(e) What kind of roads connect (i) Pamera with Gulabganj, and (ii) Gulabganj with Sirori, respectively? [2]
(f) How does the road from Gulabganj to Sirori cross the Sipu Nadi and the road from Gulabganj to Pamera cross the intervening canal. [2]
(g) What inference do you draw from Question (f) above about the amount of rainfall in this region? What else makes you to arrive at the same conclusion? [1]
(h) On which bank of the Sipu Nadi is Malgaon situated? What is the social significance of this village? [2]
(i) Write down the grid number of the region where you see considerable perennial water. What is the maximum height of the wall impounding water in the tank? [2]
(j) State two important sources of irrigation water in this region. What inference do you draw from this about the main occupation of the people in this region. [2]
SECTION - B
Attempt any two questions from this Section.
Question 2
On the outline map of Asia, provided:
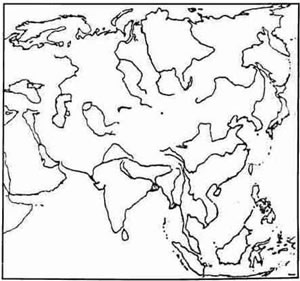
(a) Mark with a broad line the mountain range that separates the continents of Asia and Europe. [1]
(b) Shade and label the Deccan Plateau. [1]
(c) Label the river Tigris. [1]
(d) Colour (with a pencil) and label the area representing the sea in which the river Hwang-Ho falls. [1]
(e) Shade and label the area that represents the Indo-Gangetic Plain. [1]
(f) Shade and label the country called the Philippines. [1]
(g) Mark and label the river Irrawaddy. [1]
(h) Shade and label the Arabian Sea. [1]
(i) Label the river Mekong. [1]
(j) Mark with a bold line and label the Kunlun Mountains. [1]
Question 3
On that outline map of Asia, provided:
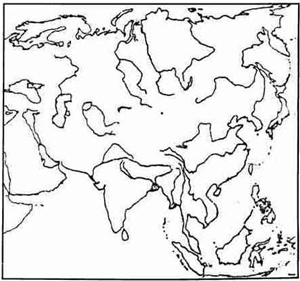
(a) Mark with a bold line, the highest mountain range of Asia and label it. [1]
(b) Shade and label the area representing the Arabian Plateau. [1]
(c) Label the river Lena. [1]
(d) Shade and label the largest inland sea lying between Europe and Asia. [1]
(e) Shade and label the area that stands for Tarim Basin. [1]
(f) Shade and label the country known as Indonesia. [1]
(g) Shade and label the Taiga vegetation belt. [1]
(h) Shade and label the Arctic Ocean. [1]
(i) Label the river Euphrates. [1]
(j) Shade and label the area representing the Pamir Knot. [1]
Question 4
On the outline map of Asia, provided:
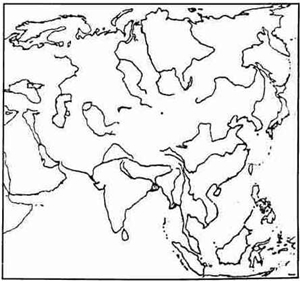
(a) Mark with a bold outline and label the mountain range in Myanmar overlooking the Bay of Bengal. [1]
(b) Shade and label the area representing the Mongolian Plateau. [1]
(c) Label the river Hwang Ho. [1]
(d) Shade the area representing the Gulf known for its huge mineral oil deposits and label it with the help of an arrow. [1]
(e) Shade and label the Altai Mountains. [1]
(f) Shade and label the Arabian Desert. [1]
(g) Shade and label the country known as the "Land of the Rising Sun". [1]
(h) Shade and label the sea of Okhotsk. [1]
(i) Label the river Indus. [1]
(j) Mark with a bold line and label the 'Tien Shan Mountains.' [1]
SECTION - C
Attempt any two questions from this Section.
Question 5
On the outline map of India and some adjacent countries provided:
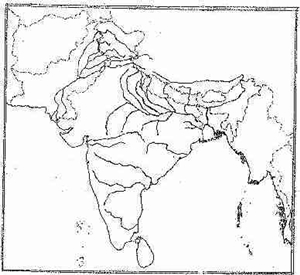
(a) Mark with a bold line and label the Karakoram Mountains. [1]
(b) Mark and label the Krishna River. [1]
(c) Shade and label the area representing the Thar Desert. [1]
(d) Mark and label the Khyber Pass [1]
(e) Shade and label the Ganga-Brahmaputra Delta. [1]
(f) Shade and label one major mica producing area. [1]
(g) Locate and label the commercial capital of Pakistan. [1]
(h) Mark and label the international port of Bangladesh. [1]
(i) Mark and label one coffee producing area. [1]
(j) Shade and label the Western Ghats. [1]
Question 6
(a) What is the time difference between the Greenwich Meridian Time (G.M.T.) and the Indian Standard Time (I.S.T.)?Explain it mathematically. [2]
(b) At a place like Bhopal one can see the mid-day sun exactly overhead twice a year, while at Vidisha, only a few kilometres North of it, one is not able to do so even once. Give the reason briefly. [1]
(c) Name the State in India through which the Standard Meridian of India, as well as the Tropic of Cancer, passes covering the longest distance. [1]
(d) A cricket match at Chennai (Madras) from October 24 to 28 had to be abandoned because of bad weather all through. As a student of Geography provide an explanation for this happening. Ensure that your explanation provides the technical name of this season in India, the atmospheric pressure conditions over the Bay of Bengal during this part of the year and the typical regime experienced in Chennai (Madras) city. [3]
(e) Name the season during which the North-East Trade Winds dominate the Indian sub-continent. [1]
(f) In which season do the above mentioned winds get completely reversed? Name the four months covered by this season. [2]
Question 7
(a) Name the four major natural vegetation belts of India. [2]
(b) What is the rainfall range of (i) Tropical evergreen rain forests and (ii) Thorn and scrub forests? [3]
(c) Name the type of forests found in the Sundarbans of West Bengal and Bangladesh. [1]
(d) Name four major groups of soil found in the Indian plains and Plateaus. [2]
(e) Give two characteristic features of the soil found most suitable for growing cotton and sugarcane in Maharashtra. [2]
(f) Which soil is found suitable for growing coffee in Karnataka? [1]
SECTION - D
Attempt any two questions from this Section.
Question 8
(a) Which is the largest mineral-based industry in India? Why is it called a key or basic industry? [2]
(b) Name four centres of this industry in the public sector concentrated in a single geographical region. With whose collaboration was each one of them set-up? [2]
(c) Why is this industry concentrated in the Chhota Nagpur region? Which is the oldest and the privately owned plant? [2]
(d) Name four large scale industries dependent on this basic industry. [2]
(e) Name two centres of the petrochemical industry in India. List two important products of this industry. [2]
Question 9
(a) What is an Agro-based industry? State two major Agro-based industries in India. [2]
(b) What has made India the world leader in jute textiles? What are the two main challenges faced by this industry today? [2]
(c) Which Agro-based industry has a tendency to migrate towards the south in India? Give reasons to justify your answers. [2]
(d) What are the four special features of the cotton textile industry in India? [2]
(e) What is a cottage industry? Why are cottage industries very important for our country? [2]
Question 10
(a) By what name is the world's largest irrigation canal in Rajasthan known today? What is its length? Name the three rivers whose water are made to flow through this canal. [2]
(b) Name four important functions discharged by a multipurpose river valley project. [2]
(c) What is the difference between surface water resources and ground water resources? Why are the latter very important for an Indian farmer? [2]
(d) Name four sources of non-conventional energy. [2]
(e) In what two ways do non-conventional sources of energy score over the conventional sources of energy? [2]