(Important Topics) Chemistry: Quantum Numbers Explained
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in

Important Topics Chemistry: Quantum Numbers Explained
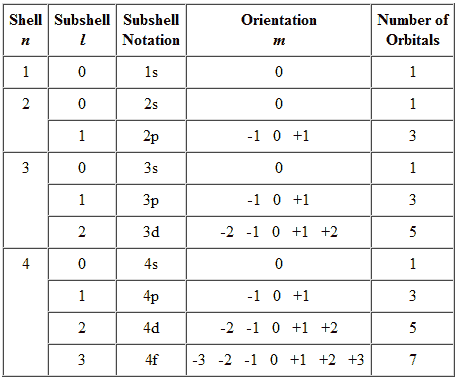
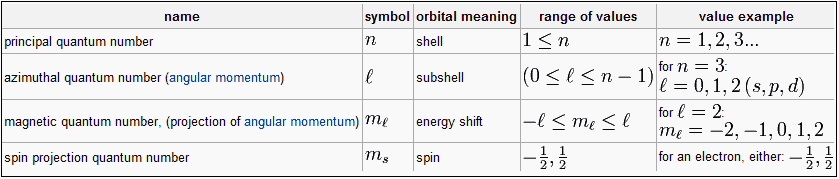
Each orbital in an atom is specified by a set of three quantum numbers (n, ℓ, m) and each electron is designated by a set of four quantum numbers (n, ℓ, m and s).
![]() Principle quantum number (n)
Principle quantum number (n)
- It was proposed by Bohr and denoted by n.
- It determines the average distance between electron and nucleus, means it denotes the size of atom.
- It determine the energy of the electron in an orbit where electron is present.
- The maximum number of an electron in an orbit represented by this quantum number as 2n2. No energy shells in atoms of known elements possess more limit 32 electrons.
- It gives the information of orbit K, L, M, N——-
- Angular momentum can also be calculated using principle quantum number.
![]() Azimuthal quantum number( ℓ )
Azimuthal quantum number( ℓ )
- Azimuthal quantum number is also known as angular quantum number.
Proposed by Sommerfield and denoted by ℓ .
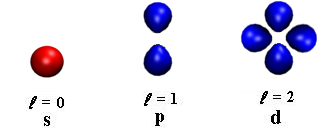
- It determines the number of sub shells or sublevels to which the electron belongs.
- It tells about the shape of subshells.
- It also expresses the energies of subshells s <p <d< f (increasing
energy).

- The value of ℓ=(n-1) always. Where n is the number of principle shell.
- It represent the orbital angular momentum. Which is equal to h/2π √ℓ (ℓ + a)
- The maximum number of electrons in subshell = 2(2ℓ+1)
s – subshell -> 2 electrons d – subshell -> 10 electrons
p – subshell -> 6 electrons f – subshell -> 14 electrons.
- For a given value of ‘n’ the total values of ℓ is always equal to the value of ‘n‘ .
![]() Magnetic quantum number (m)
Magnetic quantum number (m)
- It was proposed by Zeeman and denoted by ‘m’
- It gives the number of permitted orientation of subshells.
- The value of m varies from - ℓ to + ℓ through zero
- It tells about the splitting of spectral lines in the magnetic field i.e. this quantum number proves the Zeeman effect.
- For a given value of ‘n’ the total value of ‘m’ is equal to n2.
- For a given value of ℓ the total value of ‘m’ is equal to (2ℓ + 1).
- Degenerate orbitals : Orbitals having the same energy are known as degenerate orbitals. e.g. for p subshell Px Py Pz
- The number of degenerate orbitals of s subshell = 0.
![]() Spin quantum numbers (s)
Spin quantum numbers (s)
- It was proposed by Goldshmidt & Ulen Back and denoted by the symbol of s.
- The value of s is + 1/2 and -1/2, which signifies the spin or rotation or direction of electron on it’s axis during movement.
- The spin may be clockwise or anticlockwise.
- It represents the value of spin angular momentum is equal to h/2π √s(s+1)
- Maximum spin of an atom = 1/2 x number of unpaired electron.
- This quantum number is not the result of solution of schrodinger equation as solved for H-atom.
Graphical Representation of Allowable Combinations of Quantum Numbers