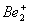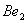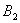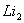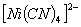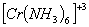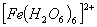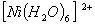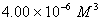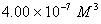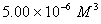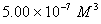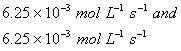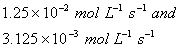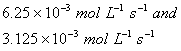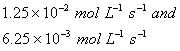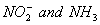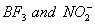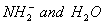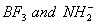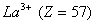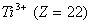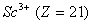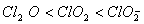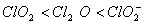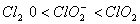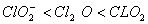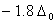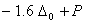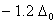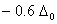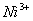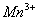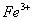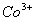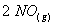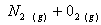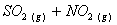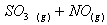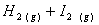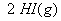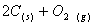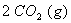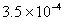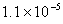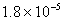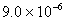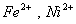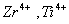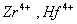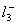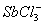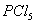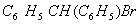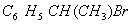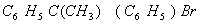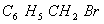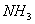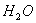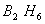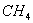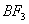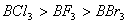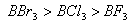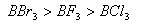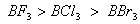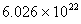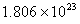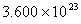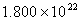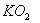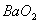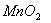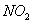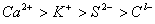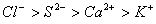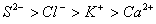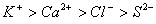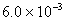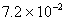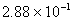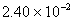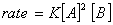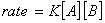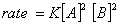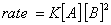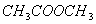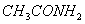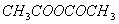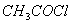(Paper) Exam Paper AIPMT 2010 | Chemistry
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Q. 1. Which one of the following species does not exist under normal conditions?
Sol:
Bond order of
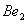 =
0, cannot exit
=
0, cannot exit
Answer : (2)
Q. 2. Which of the following complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light?
sol.
-
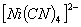 :
Number of unpaired electrons − 0
:
Number of unpaired electrons − 0 -
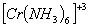 :
Number of unpaired electrons − 3
:
Number of unpaired electrons − 3 -
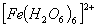 :
Number of unpaired electrons − 4
:
Number of unpaired electrons − 4 -
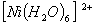 :
Number of unpaired electrons − 2
:
Number of unpaired electrons − 2
Answer : (1)
Q. 3. If pH of a saturated solution of
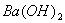 is
12, the value of its
is
12, the value of its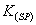 is:
is:
Sol.
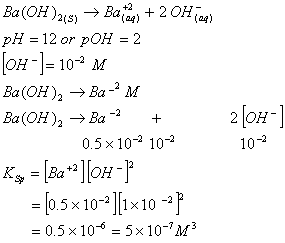
Answer : (4)
Q. 4. For the reaction
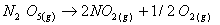 the
value of rate of
the
value of rate of
disappearance of
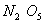 is
given as
is
given as
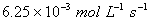 .
The rate of formation of
.
The rate of formation of
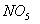 and
and
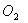 is
given respectively as:
is
given respectively as:
Sol .
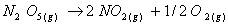
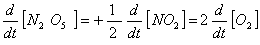
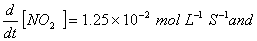
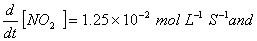
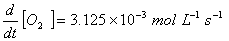
Answer : (2)
Q. 5. Which one of the following does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation?
- (+) Sucrose
- (+) Lactose
- (+) Maltose
- (-) Fructose
Sol:
Sucrose does not have free − CHO and CO groups
Answer : (1)
Q. 6. In which of the following pairs of molecules/ions, the central atoms have sp2 hybridization?
Sol .
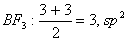
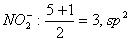
Answer : (2)
Q. 7. Liquid hydrocarbons can be converted to a mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons by:
- Oxidation
- Cracking
- Distillation under reduced pressure
- Hydrolysis
Sol:
During cracking, lower gaseous hydrocarbons are formed.
Answer : (2)
Q. 8. Given are cyclohexanol (I), acetic acid (II), 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol (III) and phenol (IV). In these the order of decreasing acidic character will be:
- III > II > IV> I
- II > III > I > IV
- II > III > IV > I
- III > IV > II > I
Sol.
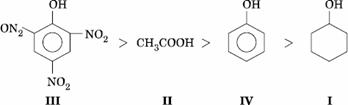
Answer : (1)
Q. 9. Which one of the following compounds has the most acidic nature?
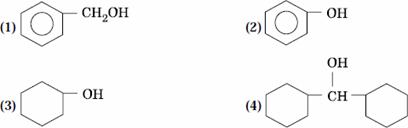
Sol:
Phenol is most acidic, the other compounds are alcohols.
Answer : (2)
Q. 10. The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ‘X’ and reaction in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are:
- X = Benzal chloride, Y = o-chlorotoluene
- X = m-chlorotoluene, Y = p-chlorotoluene
- X = o-and p-chlorotoluene, Y = Trichloromethyl benzene
- X = Benzyl chloride, Y = m-chlorotoluene
Sol.
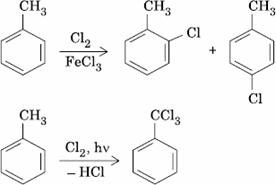
Answer : (3)
Q. 11. For an endothermic reaction, energy of activation is Ea and enthalpy of reaction is ΔH (both of these in kJ/mol). Minimum value of Ea will be:
- less than ΔH
- equal to ΔH
- more than ΔH
- equal to zero
Sol.
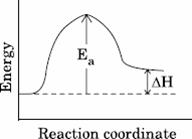
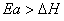
Answer : (3)
Q. 12. The correct order of increasing reactivity of C − X bond towards nucleophile in the following compounds is:
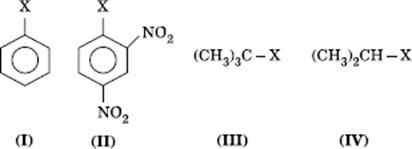
- I < II < IV < III
- II < III < I < IV
- IV < III < I < II
- III < II < I < IV
Sol:
Tertiary alkyl halide has the highest rate in nucleophilic substitution. Aryl halide has the least rate due to partial double character. Presence of − NO2 groups in ortho and para positions will increase the reactivity.
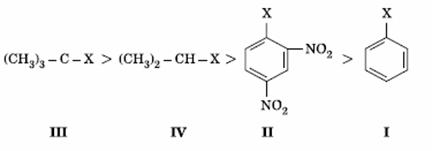
or I < II < IV < III
Answer : (1)
Q. 13. Which of the following ions will exhibit colour in aqueous solutions?
Sol:
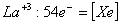
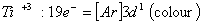
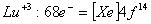
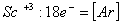
Answer : (2)
Q. 14. Acetamide is treated with the following reagents separately. Which one of these would yield methylamine?
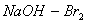
Sodalime
Hot conc.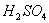
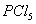
Sol .
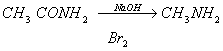
Answer : (1)
Q. 15. Aniline in a set of the following reactions yielded a coloured product ‘Y’.
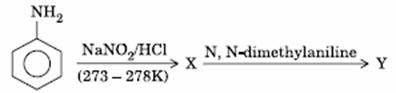
The structure of ‘Y’ would be:
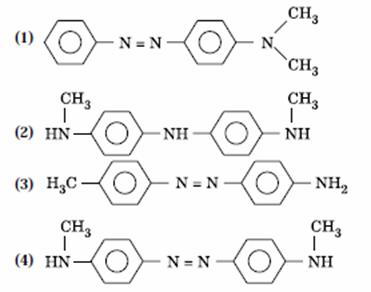
Sol.
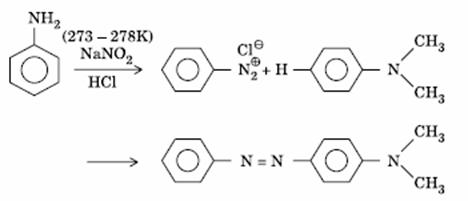
Answer : (1)
Q. 16. A solution of sucrose (molar mass = 342 g mol−1) has been prepared by dissolving 68.5 g of sucrose in 1000 g of water. The freezing point of the solution obtained will be: (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol−1)
- −0.372oC
- −0.520oC
- + 0.372oC
- −0.570oC
Sol.
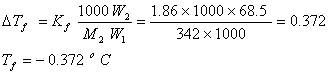
Answer: (1)
Q. 17. An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to:
- increase in ionic mobility of ions
- 100% ionisation of electrolyte at normal dilution
- increase in both i.e. number of ions and ionic mobility of ions
- increase in number of ions.
Answer : (1)
Q. 18. Oxidation states of P in H4P2O5, H4P2O6, H4P2O7 are respectively:
- +3, +5, +4
- +5, +3, + 4
- +5, +4, +3
- +3, +4, +5
Sol.
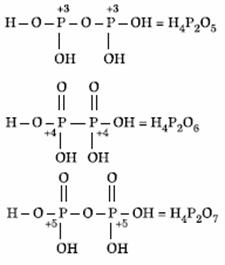
Answer : (4)
Q. 19. The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following species are:
Sol:
The correct order of increasing bond angle is
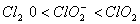
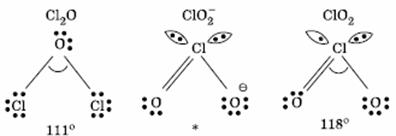
* In
 there
are 2 lone pairs of electrons present on the central chlorine atom. Therefore
the bond angle in
there
are 2 lone pairs of electrons present on the central chlorine atom. Therefore
the bond angle in
 _
is less than 118° which is the bond angle in
_
is less than 118° which is the bond angle in
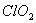 which
has less number of electrons on chlorine.
which
has less number of electrons on chlorine.
Answer : (3)
Q. 20. Which of the following alkaline earth metal sulphates has hydration enthalpy higher than the lattice enthalpy?
- CaSO4
- BeSO4
- BaSO4
- SrSO4
Sol:
Be+2 is very small, hence its hydration enthalpy is greater than its lattice Enthalpy
Correct choice : (2)
Q. 21. Crystal field stabilization energy for high spin d4 octahedral complex is:
Sol:
d4 in high spin octahedral complex
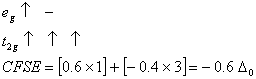
Answer : (4)
Q. 22. Which one of the following ions has electronic configuration [Ar] 3d6?
(At. Nos. Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
Sol:
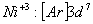
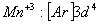
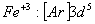
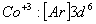
Answer : (4)
Q. 23. Which of the following statements about primary amines is ‘False’?
- Alkyl amines are stronger bases than aryl amines
- Alkyl amines react with nitrous acid to produce alcohols
- Aryl amines react with nitrous acid to produce phenols
- Alkyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia
Sol:
Aryl amines will not produce phenol on Treatment with nitrous acid.
Answer : (3)
Q. 24. An aqueous solution is 1.00 molal in KI. Which change will cause the vapour pressure of the solution to increase?
- Addition of NaCl
- Addition of
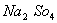
- Addition of 1.00 molal KI
- Addition of water
Sol:
When the aqueous solution of one molal KI is diluted with water, concentration decreases, therefore the vapour pressure of the resulting solution increases.
Correct choice : (4)
Q. 25. In which of the following equilibrium Kc and Kp are not equal?
Sol .
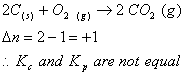
Answer : (4)
Q. 26. For the reduction of silver ions with copper metal, the standard cell potential was found to be + 0.46 V at 25°C. The value of standard Gibbs energy, ΔG0 will be (F = 96500 C mol−1)
- − 89.0 kJ
- − 89.0 J
- − 44.5 kJ
- − 98.0 kJ
Sol.
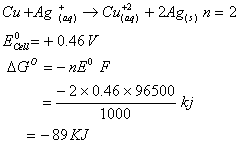
Answer : (1)
Q. 27 What is
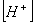 in mol/L
of a Solution that is 0.20 M
in mol/L
of a Solution that is 0.20 M
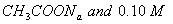
in 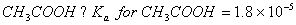
Sol .
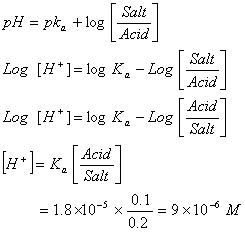
Answer: (4)
Q. 28. In a set of reactions, ethyl benzene yielded a product D.
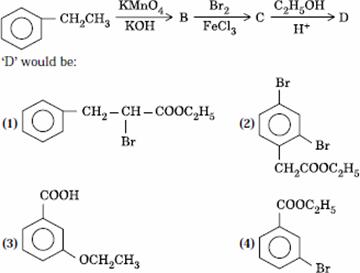
Sol.
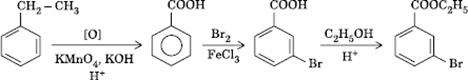
Answer : (4)
Q. 29. 25.3 g of sodium carbonate,
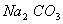 is
dissolved in enough water to make 250 mL of solution. If sodium carbonate
dissociates completely, molar concentration of sodium ion,
is
dissolved in enough water to make 250 mL of solution. If sodium carbonate
dissociates completely, molar concentration of sodium ion,
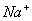 and
carbonate ions,
and
carbonate ions,
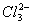 are respectively (Molar mass of
are respectively (Molar mass of
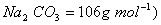
- 0.955 M and 1.910 M
- 1.910 M and 0.955 M
- 1.90 M and 1.910 M
- 0.477 M and 0.477 M
Sol .
Concentration Of 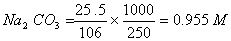
![]()
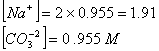
Answer : (2)
Q. 30. Property of the alkaline earth metals that increases with their atomic number:
- Solubility of their hydroxides in water
- Solubility of their sulphates in water
- Ionization energy
- Electronegativity
Sol:
Lattice energy decreases more rapidly than hydration energy for alkaline earth metal hydroxides
Answer : (1)
Q. 31. Which of the following pairs has the same size?
Sol:
ue to lanthanide contraction, the size of Zr and Hf (atom and ions) remain constant
Answer : (3)
Q. 32. In which one of the following
species the central atom has the type of
hybridization which is not the same as that present in the other three?
Sol:
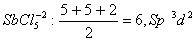
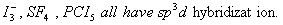
Answer : (3)
Q. 33. Which of the following represents the correct order of increasing electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for the elements O, S, F and Cl?
- Cl < F < O < S
- O < S < F < Cl
- F < S < O < Cl
- S < O < Cl < F
Sol:
O < S < F < Cl
Electron gain enthalpy − 141 − 200 − 333 − 349 kJ mol−1
Answer : (2)
Q. 34. Which one is most reactive towards electrophilic reagent?

Sol.
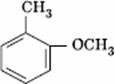
Methoxy group has the highest + M effect.
Answer : (4)
Q. 35. In the following the most stable conformation of n-butane is:
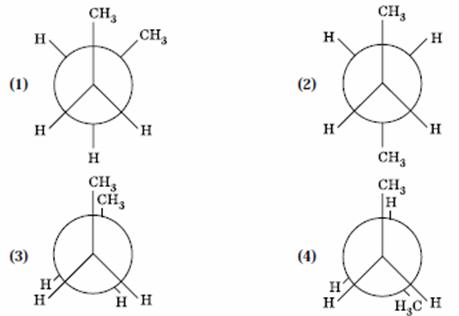
Answer : (2)
Q. 36. Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction?
Sol:
Tertiary carbonium ion formed is stabilized by two phenyl groups and one methyl group.
Answer: (3)
Q. 37. Which of the following structures represents Neoprene polymer?
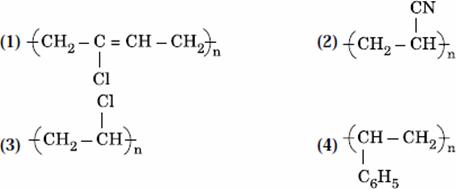
Answer : (1)
Q. 38. Which one of the following is employed as a Tranquilizer drug?
- Promethazine
- Valium
- Naproxen
- Mifepristone.
Answer : (2)
Q. 39. Which of the following reactions will not result in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?
- Reimer-Tieman reaction
- Cannizaro reaction
- Wurtz reaction
- Friedel-Crafts acylation
Answer: (2)
Q. 40. Which one of the following molecular hydrides acts as a Lewis acid?
Answer : (3)
Q. 41. The tendency of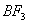 ,
,
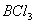 and
and
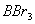 to
behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence:
to
behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence:
Sol:
p-p overlap between B and F is maximum due to identical size
and energy of porbitals, so electron deficiency in boron of
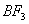 is
neutralized partially to the maximum extent by back donation. Hence
is
neutralized partially to the maximum extent by back donation. Hence
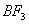 is
least acidic .
is
least acidic .
Answer : (2)
Q. 42. The number of atoms in 0.1 mol of a triatomic gas is:
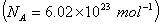
Sol:
The number of atoms in 0.1 mole of a triatomic gas =
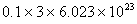
=
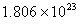
Answer : (2)
Q. 43. Which one of the following compounds is a peroxide?
Sol.
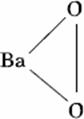
Answer: (2)
Q. 44. Standard entropies of X2,
Y2 and XY3 are 60, 40 and 50 JK−1 mol−1
respectively. For the reaction
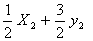
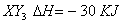 to
be at equilibrium, the temperature should be:
to
be at equilibrium, the temperature should be:
- 750 K
- 1000 K
- 1250 K
- 500 K
Sol:
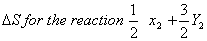
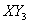
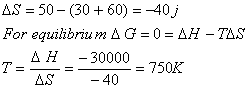
Answer: (1)
Q. 45. The correct order of the decreasing ionic radii among the following is electronic species are:
Sol:
Among the isoelectronic species
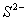 has
the highest negative charge and hence largest in size followed by
has
the highest negative charge and hence largest in size followed by
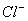 ,
,
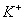 and
and
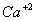
Answer : (3)
Q. 46. During the kinetic study of the reaction, 2A + B → C + D, following results were obtained:
| Run |
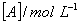 |
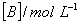 |
Initial rate of
formation of D/mol L−1 min−1 |
|
i |
0.1 |
0.1 |
|
|
II |
0.3 |
0.2 |
|
|
III |
0.3 |
0.4 |
|
|
IV |
0.4 |
0.1 |
|
Based on the above data which one of the following is correct?
Sol:
Keeping concentration of [A] constant, when the
concentration of [B] is doubled, the rate quadruples. Hence it is second order
with respect to B. Keeping the concentration of [B] constant, when the
concentration of [A] is increased four times, rate also increases four times.
Hence the order with respect to A is one.
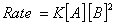
Answer: (4)
Q. 47. In a buffer solution containing
equal concentration of
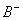 and
HB, the
and
HB, the
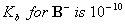 .
The pH of buffer solution is:
.
The pH of buffer solution is:
- 10
- 7
- 6
- 4
Sol.
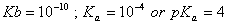
For the buffer solution containing equal concentration of
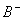 and
HB
and
HB
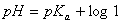
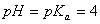
Answer: (4)
Q. 48. AB crystallizes in a body centred cubic lattice with edge length 'a' equal to 387 pm. The distance between two oppositively charged ions in the lattice is:
- 335 pm
- 250 pm
- 200 pm
- 300 pm
Sol:
For BCC lattice body diagonal is equal to a
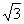
The distance between the two oppositely charged ions =
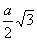
= 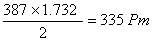
Answer : (1)
Q. 49. The existence of two different
coloured complexes with the composition of
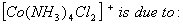
- linkage isomerism
- geometrical isomerism
- coordination isomerism
- ionization isomerism
Sol.
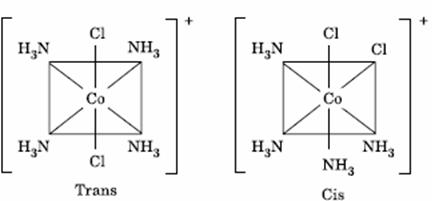
Answer : (2)
Q. 50. Among the given compounds, the most susceptible to nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group is:
Sol:
 is
the weakest base and hence better leaving group
is
the weakest base and hence better leaving group
Answer : (4)