
(Notification) NID : National Institute of Design-2020
General Information :
National Institute of Design (NID) at Ahmedabad and at its Bengaluru and Gandhinagar Extension campuses is an 'Institute of National Importance' as per the NID Act 2014 as well as an autonomous Institute under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India. As per the NID Act 2014, the Institute is a statutory authority empowered to award its own degrees- presently offering Bachelor of Design (B.Des.) of four-year duration, Masters of Design (M.Des.) of two-and-a-half year duration and PhD in Design. The Institute is also a member of the Association of Indian Universities (AIU).
NID Andhra Pradesh, NID Haryana, NID Madhya Pradesh & NID Assam are independent autonomous institutes under the DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India and offer full time Graduate Diploma Programme in Design (GDPD) of four-year duration.
Admission to all the programmes at NID is on the basis of the candidates' performance in the two-stages of Design Aptitude Test. The objective of these exams is to assess the knowledge, skills and behavioural abilities of candidates.
Stage 1: Design Aptitude Test (DAT) Prelims Design Aptitude Test (DAT) Prelims will be conducted at various test centres across India (Refer Section 7.3 of this document). Candidates should note that appearing for the DAT Prelims or being shortlisted for second stage of admission process does NOT guarantee automatic entitlement to admission.
Stage 2: Design Aptitude Test (DAT) Mains Candidates shortlisted after the DAT Prelims will be invited to appear for the Stage 2 DAT Main exam at Ahmedabad or at all campuses of NID viz Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Gandhinagar, Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, Assam and Madhya Pradesh. Exact details of the Test Centre will be mentioned in the DAT Mains Admit Card.
Note:
Candidates are fully and solely responsible to provide correct information during the application process. If it is found that any information provided by the candidate is not true, NID has the right to cancel, at any stage, the candidate's application or admission in accordance with its rules and regulations. Any direct or indirect attempt to influence the management and employees of the Institute will lead to automatic disqualification of the candidate.
The Institute has the sole prerogative to determine the procedure for each cycle of admission. In case of any matter not covered in this handbook, NID's decisions shall be considered final and binding to all the parties concerned.
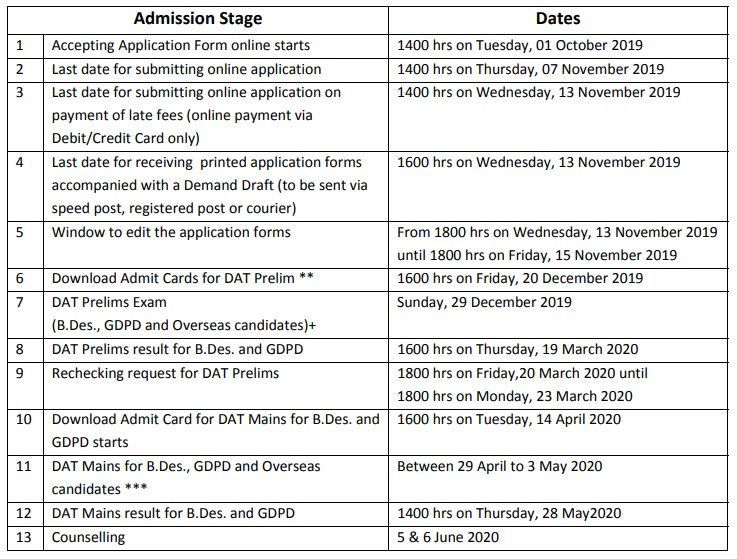
Important Dates :
Eligibility Criteria
Bachelor of Design (B.Des.) and Graduate Diploma Programme in Design (GDPD) All candidates applying for the B.Des. and GDPD programmes must fulfill the eligibility criteria of both age and education qualification.
Education Qualification :
Bachelor of Design (B.Des.) and Graduate Diploma Programme in Design (GDPD) All candidates applying for the B.Des. and GDPD programmes must fulfill the eligibility criteria of both age and education qualification.
Age limit :
- For Indian Nationals in General Category and General EWS Category: Only those candidates born on or after 1 July 2000 are eligible to apply for admission. For Indian Nationals in Reserved Category (Other Backward Class-Non Creamy Layer (OBC-NCL), Scheduled Caste (SC), Scheduled Tribe (ST): Only those candidates born on or after 1 July 1997 are eligible to apply for admission.
- For Indian Nationals in PWD Reserved Category: Only those candidates born on or after 1 July 1995 are eligible to apply for admission. For Foreign Nationals in Overseas (Supernumerary) Category: Only those candidates born on or after 1 July 2000 are eligible to apply for admission.
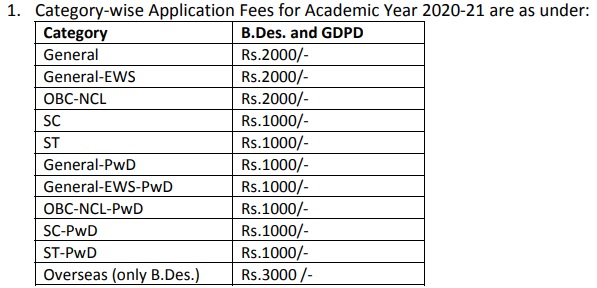
Application Fee :
How to Apply :
Step 1: Signup/Registration
1. All the candidates are required to register/sign up online before proceeding to fill the application form. This is to be done only at http://admissions.nid.edu Please provide a valid email address and an active mobile number while registering, since these contacts will be used for all future communication with the candidate.
2.Ensure that this email id and mobile number is active till 31 August 2020.
3. After registration, login credentials will be sent via an email to the registered email address (do remember to check your spam or junk folders in case you do not find the email in your inbox). In case, wrong email address and/or mobile number has been provided during signup, you are required to register afresh with the correct details.
4. Do not delete the email sent to you, as this will be useful for future reference. 5. Log in to your account using login credentials to proceed further.
Step 2: Fill the Online Application Form
1. Log in and proceed to Step 2-Application Form.
2. Fill in all the required details.
3. After filling all details, click 'Save & Proceed to go to the next section 'Upload Document'.
4. Click Save & Exit' to complete the form at a later time or date.
Step 3: Uploading your Documents and signature
1. Upload a scanned recent passport-size photograph as per the instructions. All photographs must be in JPG/JPEG format and not exceeding 100 KB in size. It must be a coloured photograph taken at a professional studio. Photographs with self composed portraits will not be accepted.
2. Upload your scanned signature as per the instructions. All signature files must be in JPG/JPEG format and not exceeding 100 KB in size. You should have your signature digitally photographed or scanned and cropped to the required size.
3. Candidates applying under the GEN-EWS category are required to upload their valid EWS Certificate issued by a competent authority. The date of issue of EWS NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF DESIGN: B.DES/GDPD ADMISSIONS HANDBOOK 2020-21 certificate must be 01 April 2019 or later. The certificate must be in JPG/JPEG format and not exceed 150 KB in size.
4. Candidates applying under the OBC-NCL category are required to upload their valid OBC-NCL Certificate issued by a competent authority. The date of issue of OBC-NCL certificate must be 01 April 2019 or later. The certificate must be in JPG/JPEG format and not exceed 150 KB in size.
5. Candidates applying under the SC and ST categories are required to upload their valid Caste Certificate issued by a competent authority. The certificate must be in JPG/JPEG format and not exceeding150 KB in size.
6. Candidates applying under the Persons with Disability (PWD) category are required to upload their valid Disability Certificate issued by a competent medical authority as per the guidelines of the Government of India. The certificate must be in JPG/JPEG format and not exceeding 150 KB in size.
7. Candidates applying under the Overseas category are required to upload the first and last page of their valid passport, clearly showing all of their personal information. The document must be in JPG/JPEG format and not exceeding150 KB in size.
8. List of documents to be uploaded by candidates of various categories at the time of applying online are summarized as unde
Design Aptitude Tests :
The Design Aptitude Tests will be conducted in two stages:
- Stage 1: Design Aptitude Test (DAT) Prelims
- Stage 2: Design Aptitude Test (DAT) Mains
7.1 Important Date: DAT (Prelims) for Bachelor of Design (B.Des.) and Graduate Diploma Programme in Design (GDPD) will be conducted on Sunday, 29 December 2019.
7.2 About DAT Prelims: The B.Des./GDPD DAT prelims paper will consist of an examination of 3 hours duration and 100 marks. This is a paper-and-pencil/pen test, conducted at the same time on the same day across all test centers. The questions asked may involve text and visuals. The question paper will be in English language ONLY. Based on the DAT Prelims scores, separate merit lists shall be prepared for each category applied for by the candidate. Only shortlisted candidates will be eligible to appear for the DAT Mains exam as per the schedule announced. Separate merit list will be prepared for Overseas candidates.
7.3 Test Centres for DAT Prelims: The DAT Prelims will be conducted in the following cities in India: Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Bhopal, Bhubaneswar, Chandigarh, Chennai, Dehradun, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Kolkata, Kurukshetra, Lucknow, Mumbai, Nagpur, New Delhi, Patna, Raipur, Ranchi, Thiruvananthapuram and Vijayawada.
NID reserves the right to add or remove any test centre and allot a test centre that may not be of the candidate's choice. A city may have more than one test centre. Any request for change of test centre will not be entertained.
7.4 About DAT Mains for B.Des./GDPD: Based on the scores obtained in the DAT Prelims, eligible candidates will be shortlisted for the DAT Mains. Admit Cards for shortlisted candidates will be available for download only on the official NID admissions website (http://admissions.nid.edu).
The DAT Mains will consist of tests in multiple formats such as in a studio set-up. The tests will be conducted over a maximum period of three days.
The total marks of the DAT Mains exam will be 100.
The question paper will be in English language ONLY.
The test centres could be any of the campuses of the various NIDs viz Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Gandhinagar, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh & Assam. Exact details of the Test Centre will be mentioned in the DAT Mains Admit Card. NID reserves the right to change the test centre.
NID will not provide accommodation for candidates appearing for the DAT Mains; candidates must arrange travel/accommodation at their own cost.
7.5 Weightages of DAT Prelims & DAT Mains for Final Result The final marks of the candidate appearing for the B.Des./GDPD programme of the National Institute of Design, will be calculated based on the weightages of the marks obtained in the DAT Prelims and DAT Mains as follows:
| Programme/Test |
DAT Prelims |
DAT Mains |
| B.Des./GDPD |
30% |
70% |
Note: Only candidates who have appeared for all the tests in both the stages will be considered eligible for the Merit List.
Announcement of Results :
In order to be considered for the merit list, a candidate must have appeared for all the tests in both the DAT Prelims and the DAT Mains.
8.1 Results for DAT Prelims: Based on the scores obtained in the DAT Prelims, separate merit lists shall be prepared for each category applied for by the candidate. Results for admission to NID for the Academic Year 2020-21 for the B.Des. (including overseas candidates) and GDPD programmes will be declared only on the official admissions website (http://admissions.nid.edu) as per the schedule announced in Section 2 of this document. The candidates' scores will also be available for viewing at this time. Separate result score cards (digital or hard copy) will NOT be provided to the candidates. In case the total marks scored by two or more candidates are the same, the following tie-break policy will be used for awarding ranks:
(i) Higher rank will be assigned to the candidate who has obtained higher marks in Part B of the DAT - Prelims.
(ii) If this does not break the tie, higher rank will be assigned to the candidate who has obtained higher marks in Part A of the DAT - Prelims.
(iii) If this still does not break the tie, then both the candidates will be assigned the same rank.
8.2 Rechecking of DAT Prelims - Exam:
8.3 Candidates Shortlisted for DAT Mains: Based on the Merit list of DAT Prelims, eligible candidates will get to appear for DAT Mains. The number of candidates shortlisted will be no less than three times in each category applied for by the candidate. Please refer to Section 3 of this handbook to see the total number of seats available. If the total scores of two or more candidates in the DAT Prelims are the same after applying tie-break policy, they will be assigned the same rank.
8.4 Final Merit List: The final common merit lists for the B.Des. and GDPD programmes will be generated category wise (Open, GEN-EWS, OBC-NCL, SC, ST, and PwD), based on the sum total of the weighted scores obtained by the candidate, viz. the DAT Prelims and DAT Mains. Separate merit list will be prepared for Overseas candidates for B.Des. programme.
Common merit list will be generated based on the percentile score.
Results for admission to NID for the academic year 2020-21 for B.Des. (including Overseas candidates) and GDPD will be declared ONLY on the official admissions website (http://admissions.nid.edu) as mentioned in Section 2 of this document. The candidates' scores and ranks will be available for viewing on the website and candidates will have to log in to the site to view their final results. Separate result scorecards (digital or hard copy) will not be sent/provided to the candidates.
In case the total marks scored by two or more candidates are the same, the following tie-break policy will be used for awarding ranks:
(i) Higher rank will be assigned to the candidate who has obtained higher marks in DAT Mains.
(ii) If this does not break the tie, higher rank will be assigned to the candidate who has obtained higher marks in Stage 1 Design Aptitude Test.
(iii) If this does not break the tie, higher rank will be assigned to the candidate who has obtained higher marks in Stage 1 Design Aptitude Test Part B.
(iv) If this does not break the tie, higher rank will be assigned to the candidate who has obtained higher marks in Stage 1 Design Aptitude Test Part A.
(v) If this does not break the tie, higher rank will be assigned to the candidate who has obtained higher marks in the question of DAT Mains exam which carries maximum marks.
The scores obtained during the application process in 2020-21 cycle are valid only for admission for the academic year 2020-21.
Scores obtained in NID's DAT exam cannot be used by any person/institution without prior permission of National Institute of Design.
Note: Obtaining a rank in the merit list does NOT guarantee admission to the programme of your choice.